Warum sich ESCR-Mitglieder auf strukturierte Befundung zur TAVR/TAVI-Planung verlassen
Finden Sie heraus, warum Mitglieder der European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR) strukturierte Befundvorlagen (Templates) für CT- oder...
5 min read
Andrea Hunt : 08 Juli 2020
Learn why ESCR members use structured reporting for CT or MRI-based planning of TAVI procedures as the basis for assisting cardiovascular radiologists in this critical treatment decision!
Structured reporting has become a tool that streamlines radiology workflows and enhances the quality of medical documentation. From guideline-based reporting in oncologic imaging such as PI-RADS 2.1 scoring for prostate cancer to cardiovascular radiology, structured reports provide quality and completeness, and improve communication. In the case of cardiovascular radiology, the pre-assessment for the TAVI procedure is one of the most well-known cases and a good example of how structured reports can improve this workflow.
For patients with aortic stenosis (AS) who are at high risk for surgery, transcatheter aortic valve replacement/implantation TAVR/TAVI represents the minimally-invasive procedure of choice to replace a narrowed aortic valve. Learn why ESCR members use structured reporting for CT or MRI-based planning of TAVI procedures as the basis for assisting cardiovascular radiologists in this critical treatment decision!
Heart disease is the number one cause of death worldwide, killing an estimated nearly 18 million people every year [1]. In the past, only inoperable patients (majority elderly) were considered when TAVI first became an option to treat aortic valve stenosis; however, this has evolved over the years to also include even some low-risk patients due to increased success in patient outcomes [2]. As of 2018, TAVR had been performed all over the world in about 400,000 patients worldwide [3].
However, "despite a reported mortality rate of 50% in the first 2 years for untreated patients, 30–40% of individuals could not receive curative treatment, deemed to be ineligible to surgery because of the high peri-operative risk," noted Dr. Marco Francone in a consensus paper from the European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR) [4].
The question for any cardiologist becomes: what criteria do we need to evaluate candidates for the procedure? Due to the age and frailty of the majority of TAVI candidates, a heart valve team of cardiac surgeons and cardiologists takes special care to assess patients. Therefore, ESCR has compiled a consensus to assess CT scan and MR imaging along with structured templates to assist in this process with a proposed list for standardization of scanning protocols.
Image: European Radiology Creative Commons CT images of a Medtronic self-expandable Corevalve (a) and Edwards Lifesciences balloon-expandable Sapien valve (d). After deployment, a self-expandable valve will conform itself to the normal annular contour, acquiring an oval cross-sectional morphology (b). Compared with a balloon-expandable valve, the self-expandable Corevalve is larger in size and contains an inflow (I), waist (w), and outflow (O) functional part (c). This outflow part is by design intended to extend into the ascending aorta, covering but not obstructing the coronary ostia. The balloon-expandable Sapien valve (d) is shorter, with a mostly circular cross-sectional contour after deployment (e) as it forces this circular morphology on the annulus through the radial forces of the expanding balloon. In contrast to the self-expandable Corevalve, it remains within the aortic sinus (f). Within both THVs, the pericardial leaflets can be appreciated as fine hypodense linear structures (arrowheads in c, f), its visibility dependent on image quality. Small interposing calcifications (arrows in b, e) have in these examples only a minimal effect on THV expansion. Reused from European Radiology Creative Commons [40].
The American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) notes that structured reports can be a mechanism to improve quality outcomes and reduce costs [5]. In the case of heart diseases, the ESCR has proposed reporting templates to assist in consistent communication between the specialists involved in the procedural planning for procedures such as TAVI. A structured report that adheres to strict guidelines for CT- and MRI-based decision planning is the best aforementioned quality and risk assessment tool.
What are the ESCR recommended CT guidelines in the TAVI reporting template?
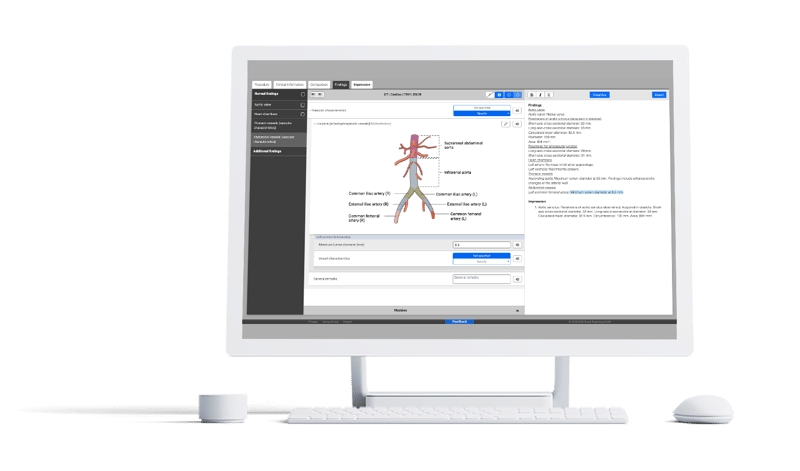
ESCR considers structured reports essential to this process to include and analyze all information necessary for TAVI planning. The standardized structure and decision tree guidance of TAVI/TAVR reporting templates allows for fast and easy assessment of the relevant medical image findings and measurements for the clinician performing the TAVI procedure.
As UK radiologist Dr. Hugh Harvey succinctly puts it: “…We owe it to our patients to do everything in our power to reduce our own errors, and we owe it to our clinical colleagues and patients to provide, clear, actionable and readable reports.” [7].
These reports are helpful to radiologists regardless of experience as they are presented completely, and in an organized fashion. Reports are created via Smart Reporting’s online platform and are more complete and more time-efficient compared to unstructured reports, the latter often requiring manual formatting, editing, and spelling correction.
Structured reporting is essential to cardiovascular radiology reporting not just in TAVI cases. In various diagnostics, from pulmonary embolism to coronary artery disease templates provide efficiency and guidance. In particular, the communication between cardiovascular radiologists and clinicians is improved.
“Structured reporting is a useful clinical tool for radiologists to capture all the necessary elements of a report. It increases the completeness of the findings and further optimizes communication between medical specialists,” explains Dr. Rodrigo Salgado, Member of the Executive Board of ESCR.
Dr. Salgado and ESCR members have been working with the templates for several years with consistently positive results. For the first time, these ESCR approved templates in the Cardio Package are available to radiologists around the world.
Dr. Alexander Bunck of the University Hospital of Cologne has also been working with structured reports for several years and has integrated the Smart Reporting platform into their RIS solution. He is also one of the German Radiological Society’s authors of their German cardio templates and a co-author of Smart Reporting’s Cardio Package.
“By introducing structured reporting, we have ensured that all clinically relevant aspects are taken into account in the reports prepared by our assistant doctors, adapted to the respective problem or pathology. The always identical structure of the respective findings reports makes it easier for me to quickly review and release the findings reports,” notes Dr. Bunck.
To see our Smart Reporting Cardio Package in action, please check out the video below!
Download our free brochure to learn how and why Dr. Salgado and Dr. Bunck rely on structured reporting templates to save time and improve their report quality. Plus, take advantage of our limited time - free TAVI template offer - when you download the brochure.
[1]Cardiovascular diseases. (2019, June 11). WHO | World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/#tab=tab_1
[2] Thomas F Lüscher, MD, FESC, TAVI is on the move! Results in low-risk patients, those with mitral disease, and those with cerebral protection, European Heart Journal, Volume 40, Issue 17, 1 May 2019, Pages 1309–1312, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz237
[3] Kourkoveli, P., Spargias, K., & Hahalis, G. (2018). TAVR in 2017-What we know? What to expect?. Journal of geriatric cardiology : JGC, 15(1), 55–60. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2018.01.005
[4] Francone M, Budde RPJ, Bremerich J, et al. CT and MR imaging prior to transcatheter aortic valve implantation: standardisation of scanning protocols, measurements and reporting-a consensus document by the European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR) [published correction appears in Eur Radiol. 2020 Mar 2;:]. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(5):2627‐2650. doi:10.1007/s00330-019-06357-8
[5]FORNELL, D. (2020, January 30). Why structured reporting is needed in cardiology DAIC. https://www.dicardiology.com/article/why-structured-reporting-needed-cardiology
[6] Francone, M., Budde, R.P.J., Bremerich, J. et al. CT and MR imaging prior to transcatheter aortic valve implantation: standardisation of scanning protocols, measurements and reporting—a consensus document by the European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR). Eur Radiol 30, 2627–2650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06357-8
[7] Harvey, H. (2018, March 28). Synoptic reporting makes better radiologists, and algorithms. Medium. https://towardsdatascience.com/synoptic-reporting-makes-better-radiologists-and-algorithms-9755f3da511a
Finden Sie heraus, warum Mitglieder der European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR) strukturierte Befundvorlagen (Templates) für CT- oder...
Learn why ESCR members use structured reporting for CT or MRI-based planning of TAVI procedures as the basis for assisting cardiovascular...
We at Smart Reporting create novel software for diagnostic medicine. We provide fully integrated image analysis and reporting in research and...